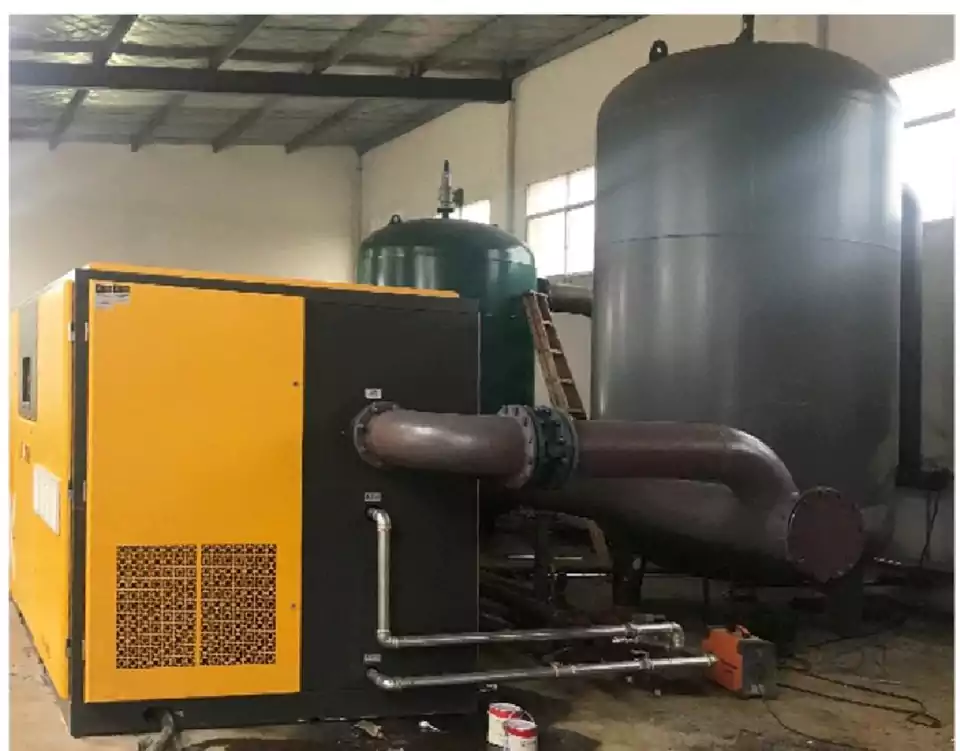
Air compressors are essential for a wide range of industrial, commercial, and personal applications. Understanding the differences between rotary screw air compressors and reciprocating air compressors can help you choose the right one for your needs.

Types of Air Compressors
Rotary Screw Air Compressors
Rotary screw air compressors are known for their efficiency and capability to deliver a continuous flow of compressed air. These compressors utilize two meshing helical screws, known as rotors, to compress the air.
The design minimizes friction and reduces energy consumption, making them suitable for demanding industrial environments.
- Continuous Operation: Rotary screw compressors can run 24/7 without the need for a cool-down period, making them ideal for high-demand applications.
- Energy Efficiency: These compressors are highly efficient in terms of electricity consumption and operational cost. For a detailed comparison of performance differences between rotary screw and reciprocating compressors, see this in-depth analysis by VMAC Air Compressors.
- Low Noise Levels: Rotary screw compressors operate at lower noise levels compared to reciprocating compressors, making them suitable for environments where noise reduction is important.
- Compact Design: These compressors have a compact footprint, allowing for easy installation in limited spaces. This is particularly beneficial for industries with space constraints.
- Longer Lifespan: With proper maintenance, rotary screw compressors can last up to 100,000 hours or more, providing a long-term solution for compressed air needs.
Reciprocating Air Compressors
Unlike rotary screw compressors, reciprocating air compressors utilize a piston mechanism to compress the air, which generally makes them more suitable for lower capacity applications. They are commonly used in smaller settings or where the air demand is intermittent.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive to purchase, they can be a more economical option for smaller operations.
- High-Pressure Applications: Capable of reaching higher pressures, reciprocating compressors are ideal for applications such as gas stations and plastic manufacturing.
- Versatility: Reciprocating compressors are available in both single-stage and two-stage configurations, allowing for different levels of air compression to suit specific needs.
- Maintenance Requirements: These compressors typically require more frequent maintenance compared to rotary screw compressors due to the higher number of moving parts.
Choosing Between Rotary and Reciprocating Compressors
When selecting an air compressor, consider your specific needs:
- Duty Cycle Requirements: Rotary screw compressors are best for continuous duty applications, while reciprocating compressors are suited for intermittent use.
- Efficiency Needs: If energy consumption is a concern, rotary screw compressors are more efficient. Learn more about their efficiency from SPRSUN’s comparison.
- Operational Environment: Rotary screw compressors are better for environments requiring clean, dry air.
- Budget Considerations: Reciprocating compressors are generally more affordable upfront, while rotary screw compressors offer long-term cost savings through energy efficiency and longer lifespans.

Maintenance and Longevity
Rotary Screw Compressor Maintenance
These units require less frequent maintenance due to fewer moving parts. Regular checks and changes of oil, filters, and separators are generally sufficient.
- Oil Changes: Rotary screw compressors typically require oil changes every 1,000 to 2,000 hours of operation, depending on the specific model and operating conditions.
- Filter Replacements: Air filters and oil filters should be replaced regularly, usually every 2,000 to 4,000 hours, to maintain optimal performance and prevent contaminants from entering the system.
- Separator Maintenance: The air/oil separator should be inspected and replaced as needed, typically every 8,000 hours or as specified by the manufacturer.
Reciprocating Compressor Maintenance
These compressors require more regular maintenance due to more wear and tear on their components.
- Frequent Inspections: Daily checks of oil levels, air filters, and safety valves are crucial to ensure proper operation and prevent issues.
- Valve Maintenance: The intake and discharge valves should be inspected and replaced as needed, usually every 1,000 to 2,000 hours, to maintain efficiency and prevent leaks.
- Piston and Cylinder Maintenance: The pistons, piston rings, and cylinders should be inspected for wear and replaced as necessary, typically every 5,000 to 10,000 hours, depending on usage.
By following the recommended maintenance schedules and using genuine replacement parts, both rotary screw and reciprocating compressors can provide reliable performance and extended lifespans.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main advantage of a rotary screw compressor over a reciprocating compressor?
A: Rotary screw compressors provide a continuous flow of air, making them ideal for applications requiring constant air supply.
Q: Are reciprocating compressors suitable for industrial use?
A: While they can be used in industrial settings, reciprocating compressors are typically better suited for smaller, less demanding applications.
Q: What type of maintenance do rotary screw compressors need?
A: They primarily need regular oil changes and filter replacements to maintain performance and longevity.
By understanding the operational differences, efficiency, and applications of these compressors, businesses can make more informed decisions. For further reading on choosing the right compressor, consider this guide by BAC Compressors.